In the realm of industrial machinery and construction equipment, hydraulic power packs are critical components that provide the necessary force to operate various systems such as pile drivers, cranes, and excavators. Among the popular options available today are Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs and electric hydraulic power packs. Each type has distinct advantages and limitations, and choosing the right one depends on the specific requirements of the application, environmental conditions, and operational preferences.
This article provides a detailed comparison between diesel hydraulic power packs and their electric alternatives, helping stakeholders make informed decisions when selecting hydraulic power solutions.
Understanding Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs and Electric Alternatives
Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs
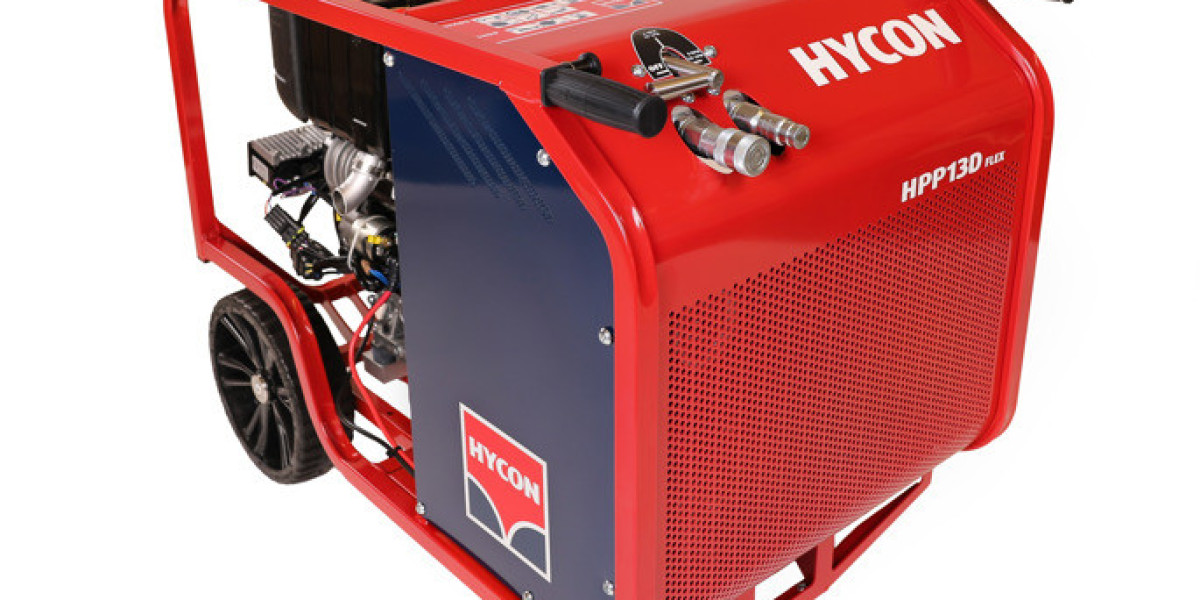
Diesel hydraulic power packs combine a diesel engine with a hydraulic pump and reservoir, creating a self-contained unit capable of generating hydraulic pressure without the need for external power sources. They are commonly used in off-grid or remote locations where electrical infrastructure is limited or non-existent.
Electric Hydraulic Power Packs
Electric hydraulic power packs operate by using an electric motor to drive the hydraulic pump. These units require a stable power supply, often from the grid or generators, and are commonly found in environments where electrical power is readily accessible.
Key Factors to Consider in Comparison
1. Mobility and Power Independence
Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs excel in mobility and independence from electrical grids. Because they are powered by diesel engines, they can operate in remote areas, construction sites, or locations lacking electricity. This makes them ideal for large infrastructure projects such as roadworks, marine construction, or mining.
On the other hand, electric power packs depend on an available electrical supply. Their mobility is limited unless paired with portable generators or batteries. In urban or developed areas where power access is guaranteed, electric units offer a convenient and quieter operation.
2. Power Output and Performance
Diesel engines in diesel hydraulic power packs typically deliver high torque and consistent power output, even under heavy loads or demanding conditions. This makes them suitable for applications requiring continuous and intensive hydraulic power, such as driving piles or operating heavy presses.
Electric hydraulic power packs provide precise control over pump speed and pressure through variable frequency drives (VFDs) and other electronic controls. They are highly efficient in applications requiring variable speeds and rapid response but may struggle to match the raw power of large diesel engines for the most demanding jobs.
3. Operational Costs and Efficiency
Operating Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs involves fuel consumption and periodic maintenance of the diesel engine, including oil changes, filters, and cooling systems. Diesel fuel costs and environmental regulations may add to operating expenses, especially in regions with strict emissions standards.
Electric hydraulic power packs generally have lower operating costs as electricity is often cheaper than diesel fuel. They require less routine maintenance since electric motors have fewer moving parts and do not need fuel handling. Additionally, electric systems tend to have higher energy efficiency, converting more input energy into useful hydraulic power.
4. Environmental Impact and Emissions
Diesel engines inherently emit exhaust gases including CO2, NOx, and particulates, contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas accumulation. In environmentally sensitive areas or urban settings, the use of Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs may be restricted or subject to costly emission control measures.
Electric power packs offer a cleaner alternative with zero local emissions. If the electricity used is sourced from renewable energy, their environmental footprint is significantly reduced. This is a critical consideration for companies aiming to meet sustainability goals or comply with stringent environmental regulations.
5. Noise and Vibration
Diesel engines are generally noisier and produce more vibration compared to electric motors. This can be a disadvantage in urban environments or sites with noise restrictions, affecting operator comfort and nearby communities.
Electric hydraulic power packs operate quietly and with minimal vibration, making them suitable for indoor use, hospitals, or residential areas where noise pollution is a concern.
6. Maintenance and Reliability
The mechanical complexity of Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs demands regular maintenance to ensure reliability. Fuel systems, exhaust components, and engine cooling require constant monitoring. However, with proper maintenance, diesel power packs are known for their robustness and durability in harsh conditions.
Electric power packs have fewer mechanical parts and thus generally experience less wear and tear. Maintenance typically involves periodic inspection of electrical components and fluid systems. Reliability is high in stable environments but can be compromised by power quality issues or electrical faults.
Applications Best Suited for Each Type
Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs: Ideal for remote construction sites, mining operations, marine pile driving, and other off-grid applications where access to electrical power is limited or unavailable. They are also preferred for heavy-duty tasks requiring continuous high power output.
Electric Hydraulic Power Packs: Best suited for factory automation, indoor machinery, urban construction projects, and applications prioritizing low noise and emissions. They are also effective in controlled environments with reliable power sources.
Conclusion
Both Diesel Hydraulic Power Packs and electric hydraulic power packs have their distinct advantages and disadvantages. Diesel units provide unmatched mobility and raw power, making them indispensable in remote or heavy-duty operations. Conversely, electric alternatives offer cleaner, quieter, and more energy-efficient operation ideal for urban or environmentally sensitive locations.